|
|||||||||
| PREV PACKAGE NEXT PACKAGE | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
See:
Description
| Interface Summary | |
|---|---|
| FarragoMetadataFactory | |
| FarragoPackage | Farrago package interface. |
| Class Summary | |
|---|---|
| FarragoMetadataFactoryImpl | |
| FarragoPackage$Hib | Farrago package implementation. |
| HibernateManyToManyLazyAssociation | Model-specific storage sub-class. |
| HibernateManyToManyLazyOrderedAssociation | Model-specific storage sub-class. |
| HibernateOneToManyLazyAssociation | Model-specific storage sub-class. |
| HibernateOneToManyLazyHighCardinalityAssociation | Model-specific storage sub-class. |
| HibernateOneToManyLazyOrderedAssociation | Model-specific storage sub-class. |
| HibernateOneToOneLazyAssociation | Model-specific storage sub-class. |
Top-level package containing all Farrago subpackages.
| Revision | $Id: //open/dev/farrago/src/net/sf/farrago/package.html#20 $ |
|---|---|
| Copyright | Copyright (C) 2005-2009 The Eigenbase Project
Copyright (C) 2005-2009 SQLstream, Inc. Copyright (C) 2005-2009 LucidEra, Inc. |
| Author | John V. Sichi |
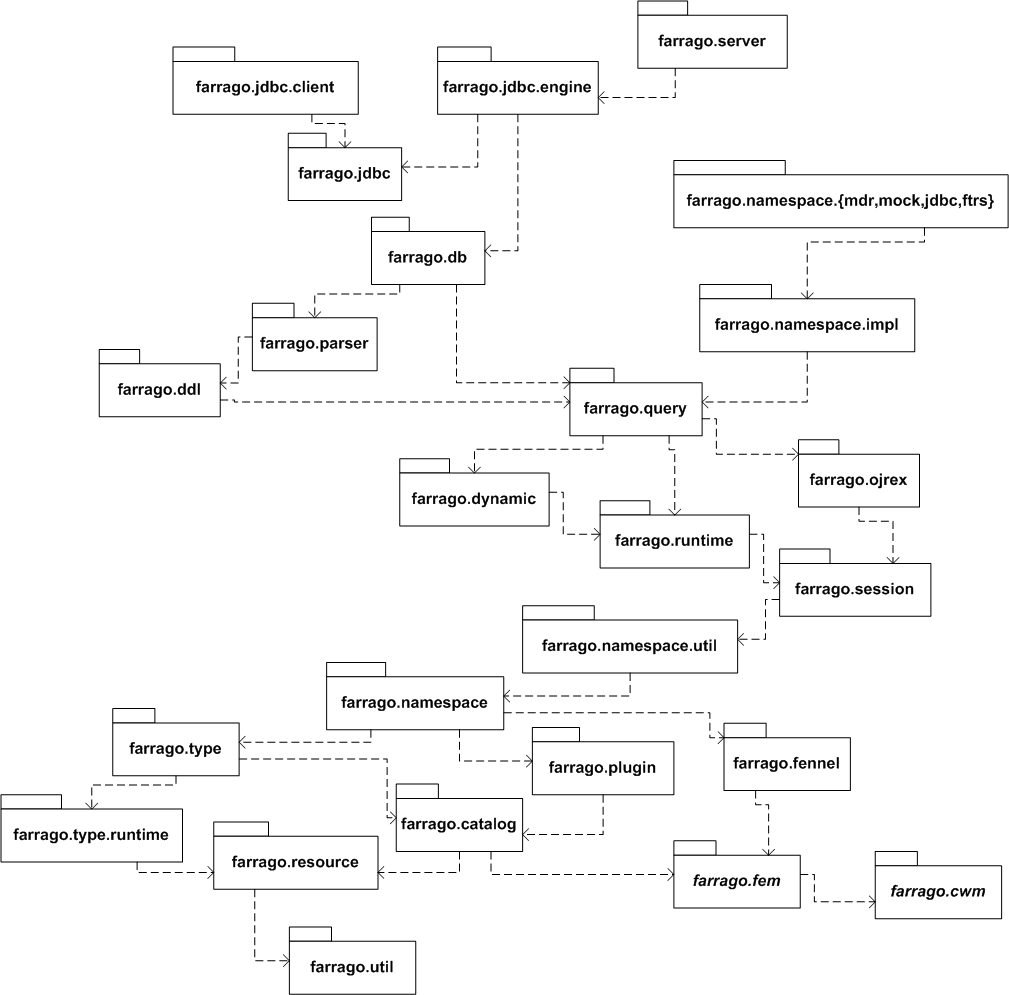
Transitive depenencies are mostly left out (so if package A depends on package B, and package B depends on C, it's implied that package A may depend on package C as well). In this context, dependency means early binding; that is, the higher-level package references the lower-level package at compile time. Packages with italicized names are interface packages.
Note that the farrago.trace package is special in that it is allowed (and in fact required) to participate in circular dependencies with other packages.
TBD: dependencies on packages like java.sql, org.eigenbase, and MDR. Also need to show com.disruptivetech.**, com.lucidera.**. And:
Dependencies are checked via the macker tool as part of Farrago checkin acceptance tests. Dependency definitions are in //open/dev/farrago/src/macker.xml.
Note that late binding is allowed to violate the layering. For
example, the util layer defines the FarragoAllocation interface. The db layer
defines class FarragoDbStmtContext, which
implements FarragoAllocation, and passes an instance to FarragoCompoundAllocation. When the
FarragoCompoundAllocation is closed, it calls back via the interface,
meaning at runtime, code in the util layer ends up calling code in the
db layer.
|
|||||||||
| PREV PACKAGE NEXT PACKAGE | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||